
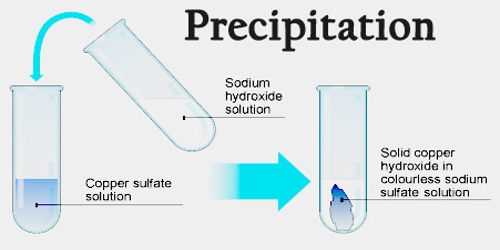
In fact, it is a highly soluble salt in water. However, in the case of KNO 3 there is no such equilibrium, so it lacks K ps. Also, knowing the K ps For an insoluble salt, the minimum amount can be calculated to precipitate it in one liter of water. This is the key to what is known as fractional precipitation. In the case of the hypothetical compound DC, its K ps it may be so high that it requires higher concentrations of D to precipitate + or from C – in solution. Therefore, by comparing this value against those of other compounds, it can be predicted which pair (eg, AB and DC) will precipitate first. Thus, the smaller a K ps, the more insoluble it is. What are the values of K ps for compounds poorly soluble in water? It is a measure of the degree of insolubility of the compound at a certain temperature (25✬). That is, by determining the solubility of one of these, that of the other and the constant K can be calculated ps. Here the solid is made up of the ions expressed in the equation however, it does not consider the solid in these calculations.Ĭoncentrations of Pb ions 2+ and I ions – are equal to the solubility of PbI 2. The term "product" refers to the multiplication of the concentrations of the ions that make up the solid: The constant of this equilibrium is called the solubility product constant, K ps. The PbI 2 establishes a balance between this and the ions in solution: Consequently, both variables benefit the appearance of PbI crystals. Furthermore, since the concentration of the salts is not very high, the temperature controls the nucleation process. Thus, as the solution cools, the nuclei have enough time to grow. To guarantee this crystal, the solution must be slightly supersaturated, which is achieved by increasing the temperature prior to precipitation. On the other hand, the maximum growth of a nucleus is reflected in a brilliant crystal. This is because the nucleation rate is greater than the growth of the nuclei. However, when this occurs, the precipitate turns out to be gelatinous, with bright hints of some crystals "wandering" through the solution.

In the same way, these particles interact with others to originate clots, and these clots with others, to finally originate the precipitate. These nuclei attract other ions, and thus it grows to form colloidal particles, responsible for the yellow cloudiness of the solution. Likewise, in other regions of the solution other ions also gather to form nuclei This process is known as nucleation. When encountering two anions I –, the cation Pb 2+ it forms a tiny nucleus of three ions, which is not enough to build a crystal.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
